Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML): Benefits, Working, & Applications
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an important technology used to secure single sign-on (SSO) and identity management. It helps organizations and service providers exchange user authentication and authorization.. information and simplifies the overall access along with enhancing security.
SAML is a great feature used by organizations to centralize identity management as well as improve the user experience by eliminating the need for multiple logins. Thus, it reduces administrative overhead for application providers who can rely on a trusted third-party service for authentication.
It is best suited for cloud environments as it offers seamless access to SaaS applications like Salesforce, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and others. So, users log in once to a central portal and gain instant access to all their authorized applications.
It was developed by OASIS and enjoys broad industry support. It is widely implemented with SAML 2.0 which is the current and the dominant version now.
What is SAML Used For?
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) serves several purposes with its primary function being simplifying and securing user access to applications and services.
It is used in both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) scenarios to share user credentials across different systems. The goal of SAML is to authenticate (verify user identity) and authorize (grant access permission) users. SAML also helps organizations with promoting interoperability which allows different identity providers and service providers to communicate easily even when they might have technical differences.
One of the most widely used applications of SAML is Single Sign-On (SSO). Single Sign-On helps users to log in once to access multiple accounts without repeated logins.
For example, if a company uses SSO with Microsoft Active Directory that integrates SAML 2.0, then it will grant employees easy access to various internal and external applications such as Microsoft Teams, Overdrive, Office365, and more.
Authentication is the foundation of security and helps systems confirm a user’s identity such as username or password. SAML supports this process and can even be used with multi-factor authentication that adds an extra layer of security to user accounts.
Authorization, the next step after authentication to access resources, is the process that determines what resources are permitted to the user to access.
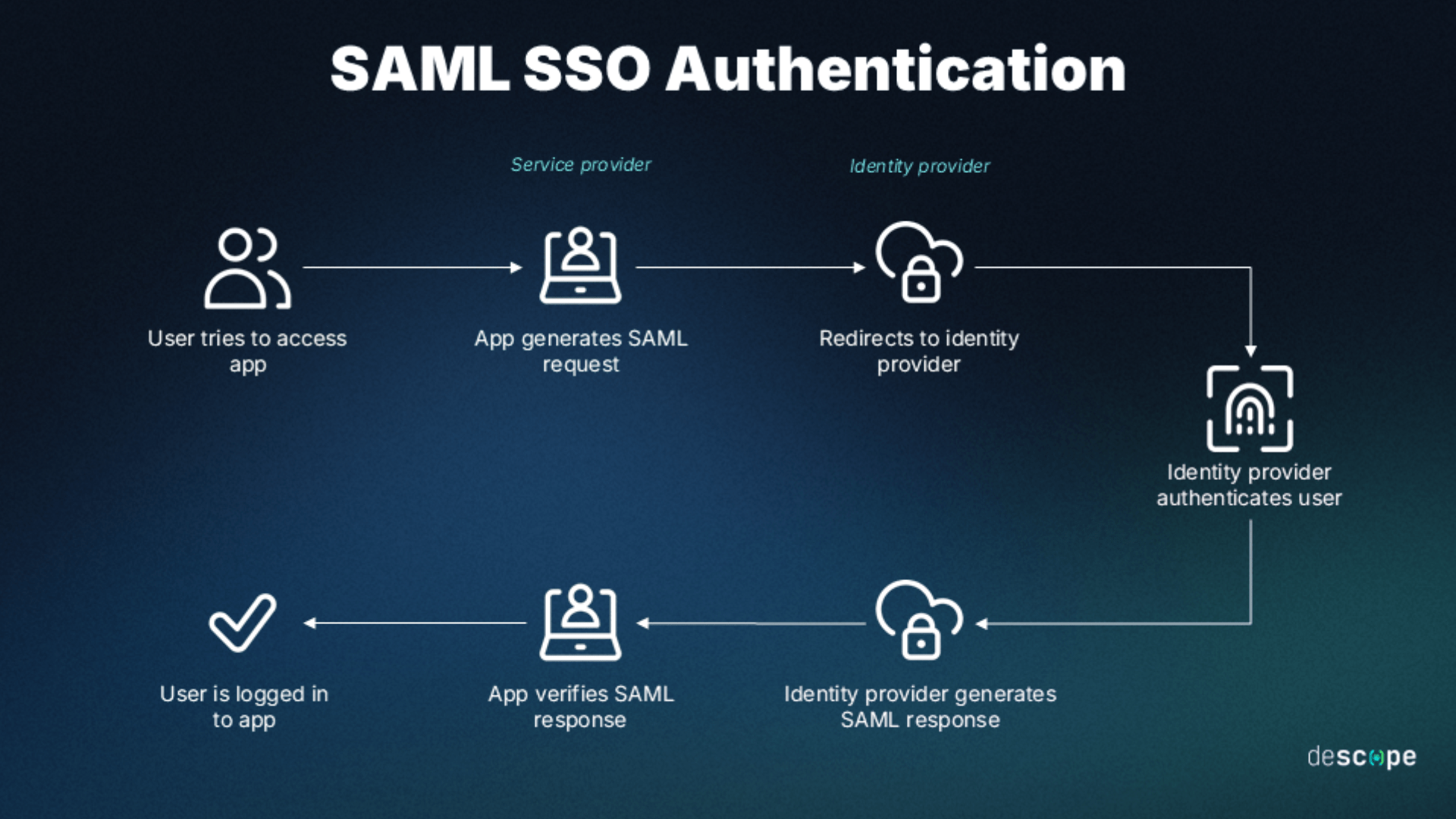
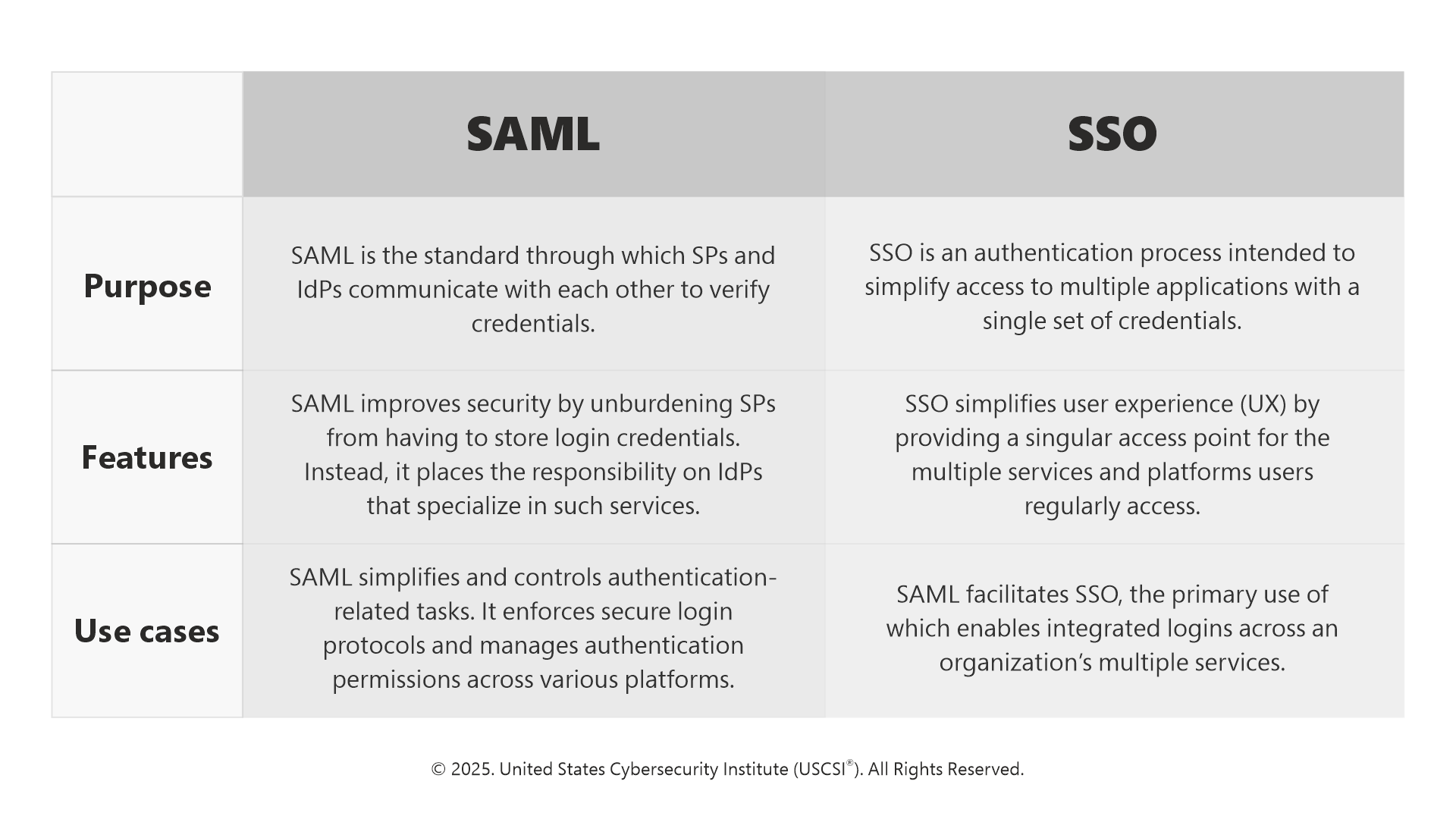
There’s a slight difference in SAML and SSO as explained in the picture below:
Different Entities Involved in SAML
In the world of SAML, a “SAML entity” is a component involved in SAML-based communication, especially those related to identity and service access.
There are mainly three types of SAML entities:
- End Users: They are the individuals who need to be authenticated to access applications and services.
- Service Providers (SPs): These are the systems that offer the services users want to access. For example, web apps, enterprise software, or anything else.
- Identify Providers (IdPs): Identity providers refer to the entities that manage and verify user identities. They handle authentication and issue assertions about users.
SAML itself provides the standard markup language for encoding authentication data exchanged between these entities. This also includes the protocols and “bindings” or “the methods of transport” that govern how SAML-compliant messages and security assertions are exchanged between end users, service providers, and identity providers.
How Does SAML Work?
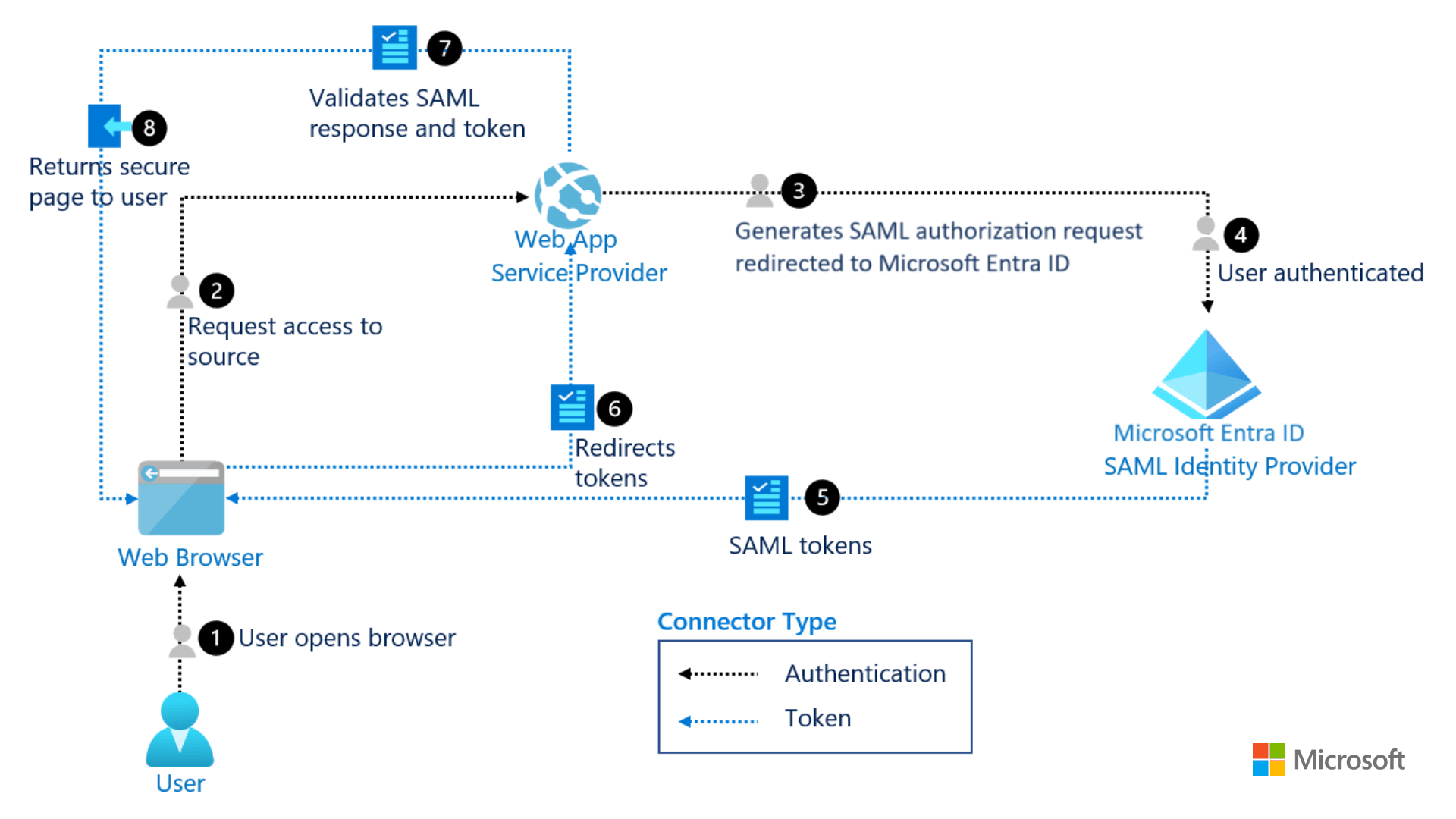
SAML is used for Single Sign-On (SSO) by securely transferring user identity information from an Identity Provider (IdP) to a Service Provider (SP). Essentially, it helps the users logged into one system easily access other systems without separate logins.
We can easily understand this through this example. Imagine a user who is already logged into their company’s network (the IdP) who wants to access a cloud application (the SP).
So, instead of requiring a second login, SAML helps with further login processes. The cloud application will recognize the user and redirect them (or their browser) back to the company network’s authentication system.
This exchange follows specific SAML protocols where authentication information is formatted as ‘assertions.’
Here is the step-by-step process involved in SAML work:
- User Request – the user attempts to access the cloud application (SP)
- Redirection to IdP – the cloud application recognizes the user isn’t authenticated there and redirects him to the company network’s authentication system (IdP)
- Authentication – the user logs in to the company network and after successful login, the network system generates a SAML assertion – a secure, digitally signed token that contains user information and permissions.
- Assertion transmission – the company network then sends this SAML assertion back to the cloud application, usually through the user’s browser
- Access granted – finally, the cloud application receives and validates the SAML assertion, and based on the information within, it grants the user access.
Benefits of SAML
SAML offers several benefits leading to its widespread adoption in the modern business environment. Here are some of them:
- Simple login credentials
SAML’s single sign-on lets users log in once and access multiple apps. This eliminates the hassle of remembering numerous passwords and ultimately enhances user experience.
- Improved security
SAML centralized user credential management with a dedicated identity provider which reduces the risk of data breaches because it basically eliminates the need for individual applications to store sensitive password data. For enhanced security, multi-factor authentication (MFA) can also be implemented.
- Interoperability
As it is an open standard, it ensures smooth integration across various systems and supports federated identity management. It simplifies user management and inter-organizational collaboration.
- Reduced Password Reset and Management Requests
SAML centralized authentication process and thus it significantly reduces the cases of forgotten passwords and frequent password resets which reduces administrative overhead.
- Cost and Time Savings
Another big advantage is a huge saving in time and money as SAML reduces administrative tasks related to account and password management. SSO leads to fewer support requests and centralized identity management helps with user provisioning that reduces IT workload and costs.
Conclusion
In the world of cybersecurity, the importance and role of SAML is increasing rapidly. It has redefined modern identity management by offering a robust and standardized solution for secure authentication and authorization. It helps with Single Sign-On enhances user experience, reduces time and cost associated with administrative overhead, and enhances overall security, especially for organizations that use cloud-based applications.
As a business or cybersecurity professional, it becomes important to understand their benefits so as to effectively integrate it in our business and minimize risk of cyber-attacks as well as improve overall user experience.