Becoming a Malware Analyst: A Complete Guide
The world of cybersecurity is growing and evolving with the introduction of newer technologies like Generative AI. These kinds of newer technologies are being used to develop new types of malwares that are difficult to detect and prevent from spreading.
This has led to the evolution of Malware Analysts jobs who have to deal with all kinds of malware and protect their organization’s systems and data. If you are interested in making a career in the Cybersecurity field, then the job of malware analyst offers an exciting and challenging as well as highly rewarding job profile.
In this article, let us explore deep into the career of a malware analyst.
What is a Malware Analyst?
Malware analysts can be considered effective cybersecurity professionals who also have advanced coding skills. To start with the basics, malware refers to malicious software that is designed to cause harm to systems and devices and/or exploit vulnerabilities. It is used by criminals to extract data from an organization’s systems or create downtime to harm business operations.
So, malware analysts are responsible for preventing this type of threat. They are specialists who are trained to identify and prevent infectious malware from affecting any system and spreading it to any other device or network.
Roles and Responsibilities
Malware analysts are part of the computer and network security teams responsible for identifying and mitigating malware-related threats including those caused by viruses, worms, bots, Trojan horses, etc. Their primary role is to analyze different types of malwares, how they are injected within an organization’s digital infrastructure, and formulate preventive plans against them.
Here is a brief overview of their roles and responsibilities
- Identifying malware in systems and networks
- Responding to incidents in case any device is infected
- Containing the spread of malware
- Classifying malware based on their threats and characteristics
- Updating themselves with the knowledge of the latest malware and making devices resilient to such malware
- Educating other technical/non-technical employees about the best practices to prevent malware attacks and damage.
Career Outlook for Malware Analysts
Now the next big question – is the career of a malware analyst secure? And what does the future of the career of malware analysts look like?
Let us understand this with some facts. According to Statista, the cybersecurity market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.56% from 2024-2028 and is expected to reach a market size of $273.6 billion by 2028. This indicates how rapidly this industry is growing and we can say the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals including malware analysts is going to be high in the coming years.
To be specific, the job of malware analyst is expected to grow by 35% by 2030, creating around 56,500 new jobs during this period, as stated by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
If we talk about Malware, then every day around 560,000 new pieces of malware are added to the already circulated 1 billion malware programs (Statista). And this number is only going to increase over the coming years. So, we can say, that malware analysts are going to be highly important cybersecurity professionals in the years to come, and this can be considered a safe as well as growing cybersecurity career option.
How Much Do Malware Analysts Make?
Not just a huge growth prospect, the job of a malware analyst is rewarding too. Here are the latest Malware Analysts' salary as on April 2024 in the United States per annum:
- Average Malware Analyst salary - $91,132 (Salary.com)
- Median salary - $145,500 (Talent.com) which can go as high as $195,750
- Annual average salary - $98,945 (Glassdoor)
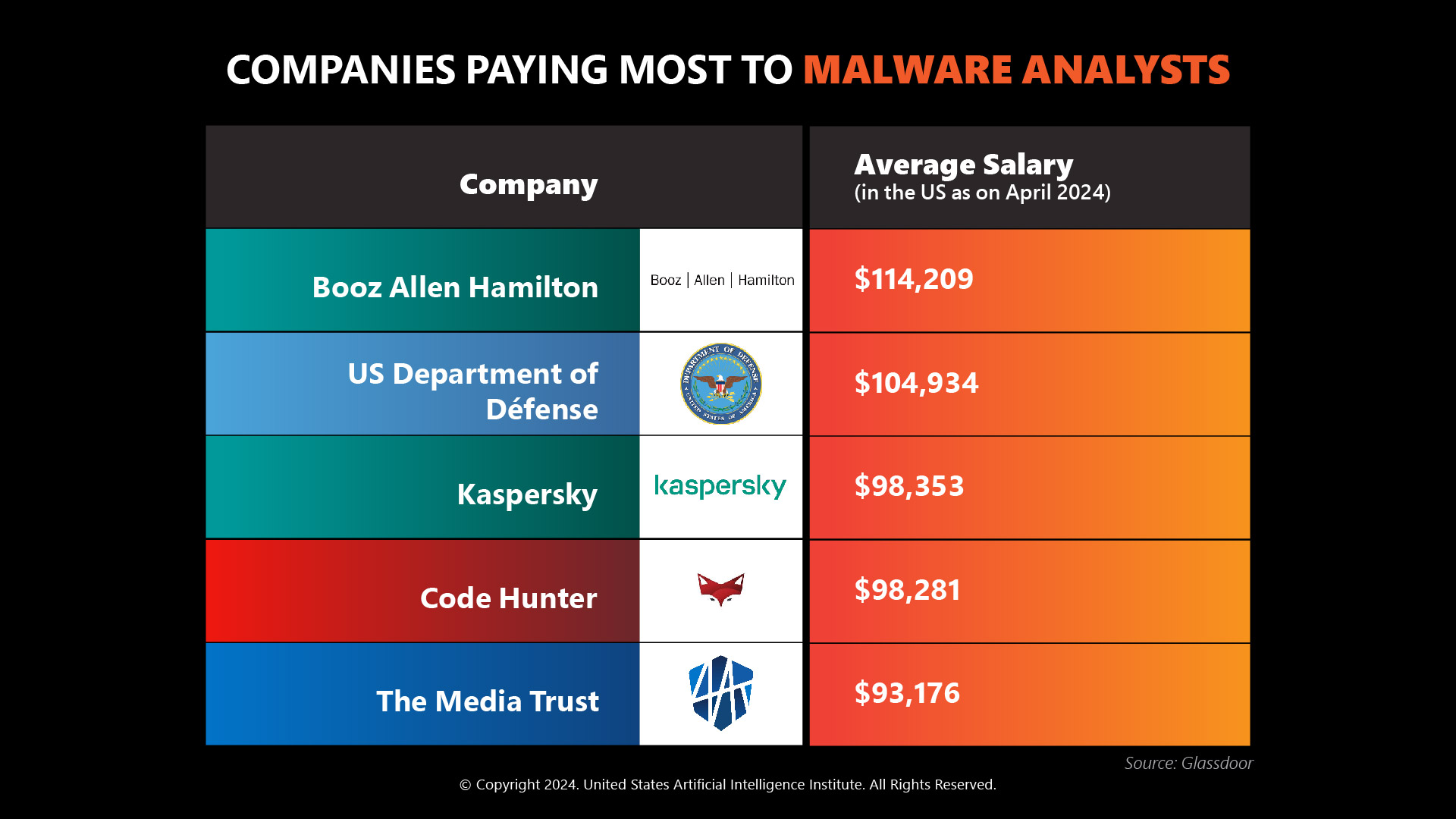
Companies paying most to malware analysts:
How to Become a Malware Analyst?
- Education Requirements
First thing first. You need to have the right educational background. To get into this career path, having the following degrees is recommended:
- Bachelor’s degree in computer engineering or computer science, information technology, computer engineering, or related field
- Master’s in computer engineering with cybersecurity specialization, or Master’s degree in cybersecurity.
- M.S. in Cybersecurity and Information Assurance, etc.
- Core/Technical Skills
You should be good at following technical malware analyst skills to perform your job efficiently.
- Basic understanding of various operating systems like MacOS, windows, and Linux and understanding of networking
- Knowledge of programming language
- Understanding of basic cybersecurity principles
- Should be able to identify, and contain zero-day malware
- Must know reverse engineering coding to mitigate the effect of malware
- Experience in working with high-level programming language
- Soft Skills Needed
Along with the above core technical skills, having the necessary soft skills is also recommended such as:
- Effective communication and collaborative skills
- Innovative and creative thinking
- Willingness to learn and upgrade with the latest and evolving technical knowledge
- Experience
Gain a minimum of 2 years of work experience in any cybersecurity job roles such as information security executive, system administrator, network administrator, etc. Experience in coding and developing can also be helpful. So, you can start with roles like computer programming and software programming as well to enter this career path.
- Certifications
Finally consider earning the best cybersecurity certifications like the ones offered by the United States Cybersecurity Institute (USCSI®) to validate your cybersecurity skills and knowledge. Certifications help professionals get the right job quickly by demonstrating their knowledge and expertise. Along with increased employability, they can also negotiate higher salaries for their job.
Conclusion
The role of malware analysts is evolving as new and upgraded forms of malware are released in the market. to enter and succeed in this career path, you must first gain the necessary education to make a solid foundation upon which you can build the technical and non-technical skills needed to become an efficient malware analyst. With relevant cybersecurity certification, your employability in this career path will be extended even further.